Differences between BSP and NPT Fittings
BSP (inch pipe thread) and NPT (American pipe thread) pipe fittings are widely used in industrial and civil pipe fields, and it is necessary to understand the differences between them.

1. Basic Definition and Origin
First, let's take a brief look at their definitions and origins.
BSP, the full name of which is British Standard Pipe, is the British pipe thread standard. It originated from the demand for standardized pipe fittings during the British Industrial Revolution and is mainly used in the UK and some European countries.
NPT, with its full name being National Pipe Thread, is the United States pipe thread standard. It emerged with the development of American industry and is mostly used in the United States and some American countries.
2. Differences in Size Specifications
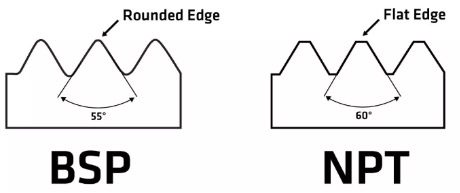
Pipe Diameter
BSP pipe fittings indicate their pipe diameter by means of inch fractions. This system has its own unique measurement rules. In contrast, NPT pipe fittings use nominal pipe diameter for expression, and this nominal value is closely related to the actual pipe diameter.
Thread Size
The BSP thread has a 55° angle with a specific pitch value, while the NPT thread features a 60° angle and a distinct pitch compared to BSP.
Matching Size
BSP fittings come with a defined tolerance range. Meanwhile, NPT pipe fittings have distinct tightness requirements compared to BSP, reflecting their different standards in the pipe fitting industry.
3. Difference in Sealing method
BSP Pipe Seals
Commonly you can use PTFE tape plays a crucial role in pipe connections. It is wrapped around the threads, effectively filling the thread gaps to create a reliable seal, ensuring leak - free performance in various piping systems.
NPT Pipe Seal
To achieve a proper seal in pipe connections, you can use materials like anaerobic sealant. The seal is created through a combination of the thread taper's design and the application of such sealing materials, ensuring a tight and leak proof joint.
Sealing Performance Comparison
Under varying pressure and temperature conditions, the sealing performance test data of BSP and NPT differ significantly. Generally, BSP is more suitable for low - pressure applications, while NPT is designed to handle high - pressure scenarios.
4. Differences in Installation and Usage
Installation Tools
Installing BSP pipe fittings typically involves using ordinary pipe pliers and similar tools. For NPT pipe fittings, although the installation tools are generally alike, their specifications may vary to suit the specific requirements of NPT fittings.
Installation Steps
When dealing with BSP pipe fittings, it is essential to coat them with sealing material prior to connection to ensure a proper seal. In contrast, for NPT pipe fittings, the key lies in accurately controlling the tightening torque during installation to achieve reliable performance.
Usage Notes
When using BSP pipe fittings, it's crucial to consider media compatibility to prevent corrosion or reaction issues. Meanwhile, for NPT pipe fittings, you need to pay close attention to how temperature impacts their sealing performance for optimal functionality.
5. Differences in Application Scenarios
Industrial Field
BSP pipe fittings find wide application in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries within the UK and Europe, thanks to their compliance with local standards. In contrast, NPT fittings are predominantly used in the oil and gas industry across the United States and the Americas.
Civilian Field
BSP pipe fittings are commonly employed in household water supply, drainage, and heating systems, ensuring smooth fluid transfer in domestic settings. Meanwhile, NPT pipe fittings serve civil gas distribution and irrigation systems, meeting the demands of these crucial infrastructure applications.
6. Conclusion
BSP and NPT pipe fittings are significantly different in size, sealing, installation and application scenarios, and the actual selection should be fully considered, otherwise it is easy to connect, seal and other problems, affecting the operation of the system.





