Understanding Pneumatic Actuators: The Power of Compressed Air in Automation
In an era where automation and efficiency are paramount, pneumatic actuators have emerged as vital components in numerous industrial applications. Harnessing the power of compressed air, these devices play a crucial role in various sectors, including manufacturing, automotive, and robotics.
What is a Pneumatic Actuator?
A pneumatic actuator is a mechanical device that converts compressed air into mechanical motion. Unlike electric actuators, which rely on electrical energy, pneumatic actuators utilize the force generated by pressurized air to create linear or rotary motion. This unique operating principle makes them ideal for environments where speed and power are essential.
How Do Pneumatic Actuators Work?
The basic operation of a pneumatic actuator involves several key components:
Air Supply: Compressed air is stored in a reservoir and supplied to the actuator through piping.
Cylinder: The core of the actuator, typically a cylindrical chamber, houses a piston that moves when air pressure is applied.
Piston: As compressed air enters the cylinder, it pushes the piston, creating linear motion. In rotary actuators, the piston is replaced by a vane or a rack and pinion mechanism, allowing for rotational movement.
Control Valve: This component regulates the flow of compressed air into the actuator, allowing for precise control over the speed and position of the actuator's motion.
When the control valve opens, compressed air fills the cylinder, forcing the piston to move. The speed of this movement can be adjusted by modulating the airflow, providing flexibility in operation.
Advantages of Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators offer several benefits that make them a popular choice in various applications:
1. Speed: They can achieve rapid actuation, making them suitable for applications requiring quick response times.
2. Force: Pneumatic actuators can generate significant force relative to their size, allowing them to handle heavy loads efficiently.
3. Simplicity: The design and operation of pneumatic systems are relatively straightforward, contributing to easier maintenance and troubleshooting.
4. Safety: Being non-electrical devices, pneumatic actuators pose less risk of sparks, making them suitable for hazardous environments.
Double Acting Pneumatic Actuator
One notable example is the Hearken Double Acting Pneumatic Actuator, which boasts efficient output torque and smooth operation in a compact design. This actuator is particularly well-suited for the operation of ball valves and butterfly valves. Its body is made of extruded aluminum, while the end caps are die-cast, ensuring durability and reliability. Moreover, every Hearken actuator is 100% factory pressure tested to guarantee the highest quality. It also provides various valve accessories, including limit switches, positioners, solenoid valves, and mounting brackets and couplings.
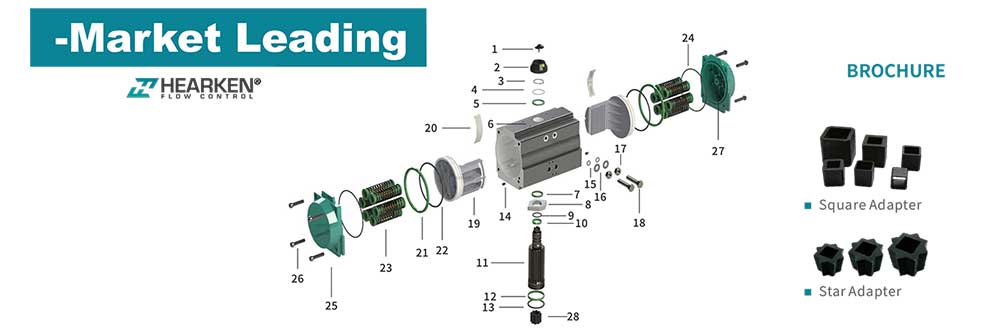
Applications in Industry
Manufacturing: Automating assembly lines, controlling valves, and managing material handling systems.
Automotive: Operating tools, presses, and robotic arms in vehicle manufacturing.
Food and Beverage: Ensuring hygienic operations in packaging and processing equipment due to their simple cleaning requirements.
Future Trends in Pneumatic Actuation
As industries continue to embrace automation, the demand for pneumatic actuators is expected to rise. Innovations in materials and design are leading to more efficient and compact actuators, while advancements in control technology are enhancing their precision and responsiveness.
Moreover, the integration of smart technologies, such as IoT (Internet of Things), is paving the way for smarter pneumatic systems that can provide real-time data and diagnostics, further optimizing performance.
Conclusion
Pneumatic actuators are indispensable tools in the modern industrial landscape. Their ability to convert compressed air into mechanical motion efficiently makes them a cornerstone of automated systems. As technology evolves, these devices will undoubtedly continue to play a critical role in enhancing productivity and efficiency across various sectors.
Understanding the mechanics and advantages of pneumatic actuators not only assists engineers and manufacturers in optimizing their processes but also highlights the ongoing importance of automation in driving industrial innovation.






