What is the Difference Between Single-Acting and Double-Acting Positioners?
What is a single-acting and double acting positioner?
Understanding Single-Acting Positioners
Definition: Single-acting positioners control pneumatic actuators by allowing air to enter only one side of the actuator.
Application: These positioners rely on a spring return mechanism to bring the actuator back to its default position and are commonly used in applications where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are priorities.
Understanding Double-Acting Positioners
Definition: Double-acting positioners control actuators by allowing air to flow to both sides of the actuator, enabling precise bidirectional movement.
Application: Without relying on a spring, double-acting positioners provide better stability and control, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications and situations where precise positioning is required.

Key Differences Between Single-Acting and Double-Acting Positioners
1. Control Mechanism
Single-acting positioners: Use a spring to return to the default position when air pressure is removed, making control simpler and straightforward.
Double-acting positioners: Rely on air pressure on both sides of the actuator, providing smoother and more flexible bidirectional control without a spring.
2. Cost and Maintenance
Single-acting positioners: Typically more affordable and require less maintenance, making them suitable for applications with basic positioning needs.
Double-acting positioners: Generally more expensive but provide superior control, making them a valuable investment for high-precision applications.
3. Applications and Preferences
Single-acting positioners: Ideal for simpler, low-cost applications where precision is not a primary concern but budget and ease of use are important.
Double-acting positioners: Ideal for heavy-duty applications where precise control and stability are essential. Suitable for industries that require enhanced performance and accuracy.
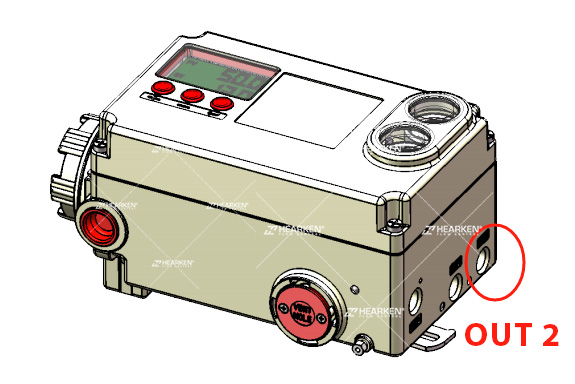
How Can a Positioner Be Changed from Double-Acting to Single-Acting?
Changing a positioner from double-acting to single-acting is straightforward. Simply block the port labeled "Out 2" and the positioner will operate as a single acting unit.
Can a Positioner Be Changed from Single-Acting to Double-Acting?
No, a single-acting positioner cannot be modified to function as a double-acting one.
Conclusion
When choosing between single-acting and double-acting positioners, consider your application needs, budget, and control requirements. Double-acting positioners offer high precision, while single-acting models provide simplicity and cost savings for less demanding uses.





